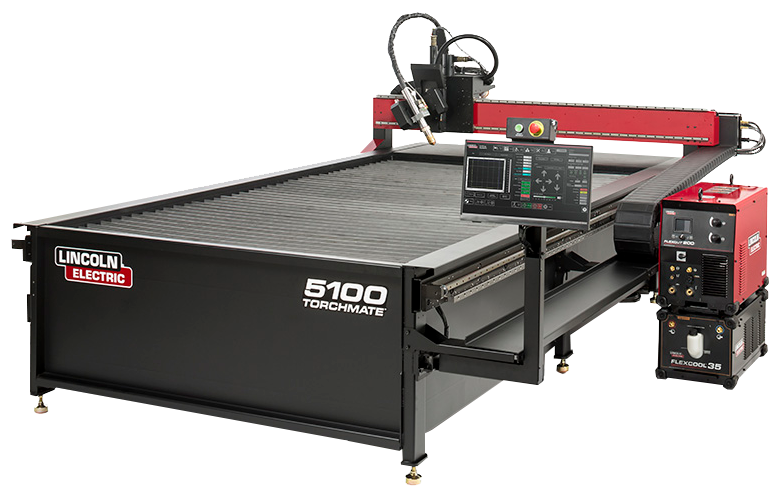
Basic Cut Troubleshooting
Bevel Basics
Bevel is caused by the motion of the plasma gas as it is emitted from the nozzle. In plasma cutting it is unavoidable. High definition plasma produces less bevel than a standard cutter.
Torch height, air pressure, quality of air, direction of cut, and consumable condition all contribute to how much bevel a cut has.
In the process to create a plasma arc for cutting the gas must be shaped into a vortex. Because of this an arc will have a direction of rotation. This will cause one side of the cut to have more bevel than the other. To ensure that the best bevel is on the part, proper direction of travel is necessary.

The direction of cuts are referred to as conventional and climbing. In a conventional cut the torch will go counter-clockwise on outside cuts and clockwise on inside cuts. A climbing cut is the opposite. For plasma the best bevel is achieved by using a climbing cut. Basically the best cut being to the right of the direction of travel.

Corners can also have a bit more bevel than a normal cut. This is caused when the machine slows down to make the direction change. This can be minimized by adjusting ramping rates and start stop values. It is also possible in some cases to use a lower amperage to allow for slower travel speeds. This reduces the amount of slowdown through corners. Sharp corners can be achieved by cutting a larger shape that puts the slow down and acceleration of the machine into a scrap area. This cut is used more on thick materials where the corner bevel is increased dramatically.

Consumables if not replaced regularly can cause bevel. If a tip wears out or slag builds on it the air flow is redirected in ways that can cause random bevel and inconsistent cut quality. Always check consumables when troubleshooting bevel. The easiest way to reduce bevel is by cutting at the proper speed and height for the material and amperage that is being cut. Constant air pressure and volume that is clean and dry also decreases the bevel. Using consumable in good condition also prevents excessive bevel.
How Torch Positon Affects Bevel

What Causes Bad Cuts
Instances where the metal was not fully cut indicate a few different problems. If the ground clamp was not properly attached to the material this can happen. A similar cut can happen if there was a drop in air pressure, moisture in the air line, or a drop in power. A third cause is if the torch contacts the material, most plasma cutters will go into a low power mode when this happens causing the cut not to penetrate all the way.
When a machine’s performance suddenly changes or degrades gradually from one part to another this generally indicates something mechanical has changed. In cases like this check tightness of belts and set screws. Ensure that the gear to gear rack spacing is adjusted properly. The square of the gantry to the table can also cause parts to be out of shape.

When a machine’s performance suddenly changes or degrades gradually from one part to another this generally indicates something mechanical has changed. In cases like this check tightness of belts and set screws. Ensure that the gear to gear rack spacing is adjusted properly. The square of the gantry to the table can also cause parts to be out of shape.

A cut where the path does not return to the start point indicates mechanical slipping or binding. In some cases it will be clear which axis is losing position. Examine the particular axis for loose set screws, loose belts, or physical obstructions.

In some cases the slipping in one direction will be offset by slipping in the opposite direction of travel. This allows the part to be cut out but the tool path was not followed correctly. Set screws, belts, gear spacing, and square of the table should be checked.
When the machine begins to move before a pierce is completed the cut will not complete. In this case the dwell time or pierce delay must be adjusted to allow for enough time to pierce the material.